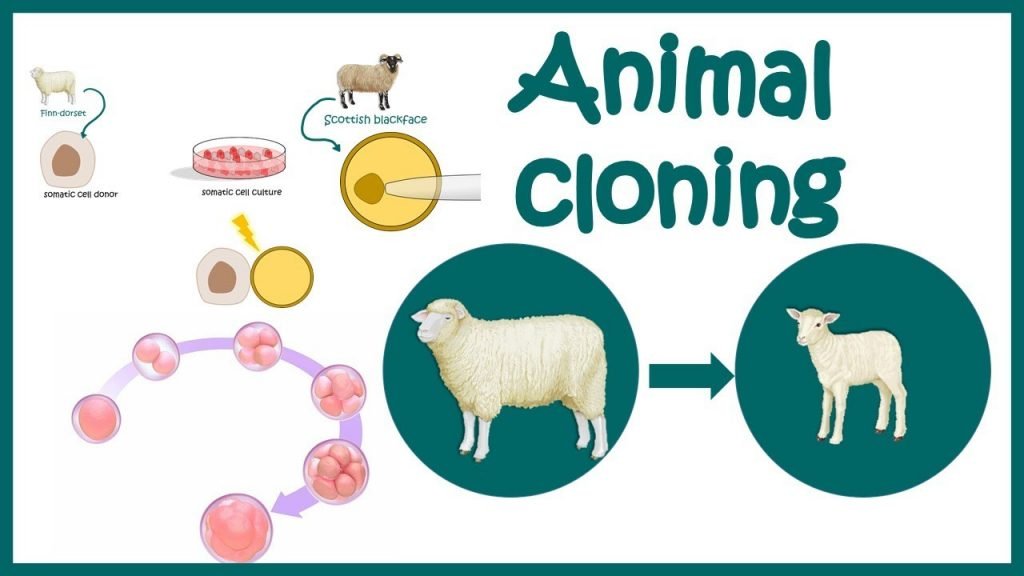
Animal cloning is the process of creating an identical genetic copy of an animal. The technique has been used to clone a variety of animals, including sheep, cows, and dogs. While animal cloning has the potential to benefit society in many ways, it also raises a number of ethical concerns. This article will explore the ethical implications of animal cloning, including the impact on animal welfare, the potential for genetic abnormalities, and the impact on biodiversity.
Animal Welfare
One of the primary ethical concerns associated with animal cloning is the impact on animal welfare. Cloning can be a stressful and painful process for animals. In some cases, the cloning process can result in the death of the cloned animal or the surrogate mother. In addition, cloned animals may experience health problems, such as respiratory problems and immune deficiencies. These health problems can result in a lower quality of life for the cloned animal.
Genetic Abnormalities
Another ethical concern associated with animal cloning is the potential for genetic abnormalities. Cloning can result in genetic defects, such as developmental abnormalities and birth defects. In addition, cloned animals may be more susceptible to certain diseases and health problems. These genetic abnormalities can have a significant impact on the health and well-being of the cloned animal.
Biodiversity
Animal cloning also raises concerns about the impact on biodiversity. Cloning can reduce genetic diversity within a species, which can make the species more vulnerable to disease and environmental changes. In addition, cloning can also lead to the loss of genetic diversity within a population, which can have long-term ecological consequences.
Animal Rights
The use of animal cloning also raises concerns about animal rights. Some people argue that cloning is a form of exploitation and that it is unethical to use animals for human purposes. Others argue that animals have a right to life and that cloning is a violation of that right. In addition, some people argue that cloning is a form of genetic engineering and that it is unethical to manipulate the genetic makeup of animals.
Religious and Cultural Beliefs
Animal cloning also raises concerns about religious and cultural beliefs. Some people believe that cloning is a violation of the natural order of things and that it is a form of playing God. Others believe that cloning is a form of disrespect for the natural world and that it is a violation of the spiritual beliefs of many cultures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, animal cloning raises a number of ethical concerns, including the impact on animal welfare, the potential for genetic abnormalities, the impact on biodiversity, animal rights, and religious and cultural beliefs. While animal cloning has the potential to benefit society in many ways, it is important to carefully consider these ethical implications before proceeding with the use of this technology. It is important to approach animal cloning with caution and to carefully consider the potential benefits and risks associated with this technology. Ultimately, the decision to clone animals should be based on a careful consideration of the ethical implications, as well as the potential benefits and risks to both animals and humans.